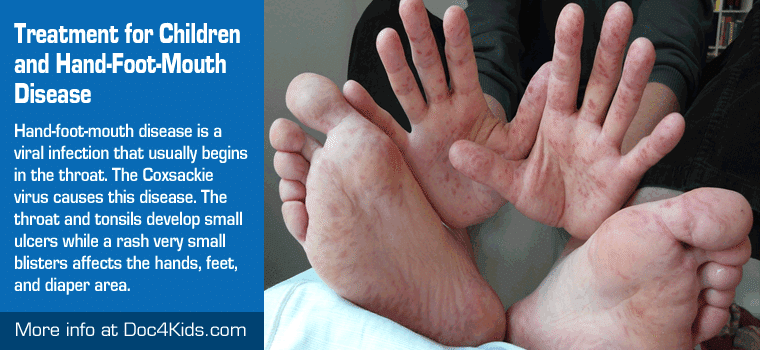
Hand-foot-mouth disease is a viral infection that usually begins in the throat. The Coxsackie virus (a member of the Enterovirus family) causes this disease. The throat and tonsils develop small ulcers while a rash with characteristic vesicles (very small blisters) affects the hands, feet, and diaper area. This is usually a mild illness with the rash healing in 5 to 7 days. The actual incidence is unknown, but hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a relatively common infection in children. Another Coxsackie virus infection with a high incidence and related features is herpangina. This is characterized by painful ulcers in the mouth and throat, but does not have a rash on the hands, feet or buttocks. The most important risk factor is age. The infection typically affects young children, but can be seen in adolescents and occasionally adults. The outbreaks occur most often in the summer and fall.
Symptoms
- Fever
- Sore Throat
- Ulcers in the throat, mouth and tongue
- Headache
- A rash with vesicles (small blisters — 3-7 mm) on hands, feet, and diaper area. The vesicles are typically on the palm side of the hands, the sole side of the feet, and are very characteristic in appearance. The vesicles are also tender or painful if pressed.
- Loss of appetite
Treatment
Since a virus causes this disease, there is no specific treatment for the infection other than symptomatic relief of symptoms. Treatment with antibiotics is not effective, and is not indicated. Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen may be used to treat any fever. Aspirin should not be used in viral illnesses in any children since this may lead to Reye’s Syndrome. Salt water mouth rinses (1/2 teaspoon of salt to 1 glass of warm water) may be soothing if the child is able to rinse without swallowing. Ensure that an adequate fluid intake occurs because swallowing may be painful and a child could become dehydrated. Extra fluid is needed when a fever is present. The best fluids are Pedialyte®, Jell-O®, cold drinks, popsicles, and cold milk products, especially ice cream or sherbet. Many children refuse juices and sodas, for example, because their acidity causes burning pain in the ulcers. You may offer a soft diet for a few days. Your child may benefit from a Maalox/Benedryl Slurry for pain relief. Mix equal amounts of Maalox (coats and soothes the gums and mucosa) and Benedryl (acts as a topical anesthetic). After mixing in a 1:1 proportion, paint the area that is inflamed as often as needed but not before every 2 hours.
Expectations (prognosis)
Generally, complete recovery occurs in 5 to 7 days. Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease is quite contagious and many of your child’s friends may get the illness. The incubation period after contact is 3 to 6 days. The spread of the disease is extremely hard to prevent. There is no need to isolate the child. Most children are contagious from 2 days before the onset of the rash until 2 days after the rash is through.
Complications
- Dehydration can occur because the mouth lesions can cause pain with swallowing.
- Possible febrile seizure
Calling The Office
Apply home treatment and call us if there are signs of complications, such as pain in neck or arms and legs. Other times to call include: when a high fever is not reduced by medication, signs of dehydration occur such as dry skin and mucus membranes, weight loss, irritability, lethargy, and decreased amount of urine (no output for more than 8 hours) or dark urine. Emergency symptoms include convulsions.
Prevention
Avoid contact with people with known illness. Strict hand washing is important if in contact with infected children.